As ERGs become increasingly integral to the employee experience, they have also grown in value to employers. In this post, two experienced ERG program leaders share insights on what it takes to foster ERGs and ensure success in the eyes of employees and business leaders.
Sometimes called affinity groups or business networks, employee resource groups (ERGs) aim to foster inclusivity in the workplace by creating a space for employees who share a common interest or affinity to support one another and raise awareness.
In recent years, ERGs—or employee resource groups—have grown in popularity among employees. Between 2011 and 2017, participation in resource groups among companies who ranked in DiversityInc’s Top 10 leapt from 29% to 38%.
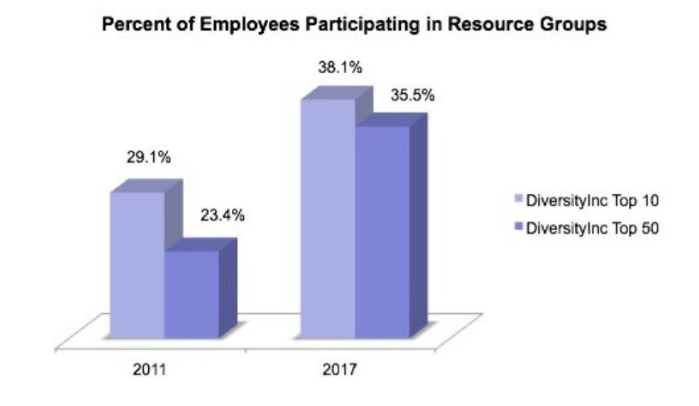
Source: DiversityInc
ERGs have also grown in value for companies, who have come to understand that employee resource groups enhance the employee experience. By enabling employees to connect, share, contribute, and support one another, ERGs can make the work environment friendlier and more welcoming.

Source: SHRM. Are Employee Resource Groups Good for Business. August 25, 2016.
Because of this impact on workplace culture, ERGs lend powerful support to critical business and talent objectives—increasing employee retention, developing new leaders, and helping recruit high-quality diverse talent. Many companies also rely on their ERGs to foster innovative thinking and break into or expand into new markets.

Source: SHRM. Are Employee Resource Groups Good for Business. August 25, 2016.
HOW CAN ERGs WORK VIRTUALLY? | ‘5 Virtual ERG Lessons Learned From Lockdown‘
7 Best Practices for a Successful ERG Program
Launching or building a program to maximize the value of ERGs or affinity groups isn’t easy. It takes organizational commitment, thoughtful planning, and strong leadership.
We asked two seasoned diversity leaders for insights and examples of best practices for successful ERGs. Affirmity’s Pamela Pujo and Juna Jones-Moore, who leads D&I at GameStop, have led successful ERG programs for a global enterprise, guiding the formation of groups and helping ensure alignment on company objectives.
Here are their 7 key best practices for implementing and managing successful ERGs, with examples and insights from GameStop.

1. Create a Mission Statement and Goals for Each ERG
Any time people come together in service of a common purpose, the group should create a mission statement to serve as its guiding principle. ERG mission statements should align with the group’s purpose and the company’s business objectives.
Once the mission statement is clearly defined, the group can formulate goals. Goals, in turn, serve as the foundation for the ERG’s business plan and guide the group in carrying out its mission.
While the mission statement endures over time, ERG goals require annual review to ensure they remain aligned with the needs of their members, company policies, and business objectives.
At GameStop
Formalized in 2015, GameStop’s ERG program grew out of a 2011 focus group of “diversity champions.” Its mission is to foster a diverse, inclusive workplace supported by GameStop’s values, with four key goals:
- Develop future leaders
- Increase employee engagement
- Expand market reach and recruiting network
- Create opportunities for GameStop leaders to build cultural competence.
2. Establish Guidelines and a Structure for ERGs
Guided by its mission and goals, each ERG should develop guidelines that define its structure and operation, including
- How chapters are established
- How finances and funding are managed
- How meetings function
- How leaders are selected.
READ THIS | ‘Successful Employee Resource Groups: 5 Strategies from Top Companies.’

3. Define ERG Leadership Roles
Like any organization, an ERG needs a strong, capable leader to drive growth and engage members as active participants in its activities.
The best way to ensure your business networks are led by top performers is to make the role of ERG leader an attractive one. For example,
- Exposure and access to executive sponsors and company leaders
- Opportunities to learn and hone leadership skills, to apply in their current role, or better position themselves for advancement
- Influence over the ERG’s direction and activities to support members and business objectives.
As organizations have come to recognize the importance of strong leadership to ERG success, many organizations have begun appointing leaders based on their capabilities and other criteria.
At GameStop
GameStop ERG leaders are appointed based on sales performance and, more importantly, on their affinity with a team of associates who reflected a community that GameStop serves.
4. Engage Executive Sponsors
In addition to its leadership, each ERG needs to secure an executive sponsor and define expectations for the role. Typical responsibilities include
- Serving as a public advocate for the group
- Influencing other company leaders to lend support to the group’s goals
- Mentoring ERG members.
- Effective executive sponsors exercise their influence as catalysts for growth and as a connection to sustained funding, business relevance, and impact.
By serving as an executive sponsor of an ERG, your company’s top leaders gain an opportunity to engage directly with employees across the organization. They may derive further benefit by forming a diversity leadership council through which they can share best practices and hold each other accountable.
MORE ON ERGS AND EXECUTIVE ENGAGEMENT | ‘Maximizing the Value of ERGs: Expert Answers to 7 Burning Questions‘
5. Track and Measure the Effectiveness of ERGs
Like any other company initiative, measurement is essential to effectively managing individual ERGs and the ERG program as a whole.
Each of your ERGs should identify key metrics to track and report on trends in member involvement, including
- Group membership
- Event attendance
- Participation in ERG program (mentoring, community service, etc.)
- Budget performance.
Similarly, your HR leadership or executive diversity council will want to track the effectiveness of ERGs against company initiatives. Ideally, your organization will capture baseline data before launching an ERG program so you can see how the program influences talent metrics such as
- Recruiting event representation
- Retention rates
- Employee engagement levels
- Hiring rates for diverse candidates
- Employee promotion rates.

6. Promote Allyship and Collaboration among ERGs
Because the underlying principle of ERGs is one of inclusion and bringing employees together. So they’re perfectly positioned to build a culture of allyship among employees and to foster collaboration across the organization.
The best ERGs welcome employees from all backgrounds, and they cultivate cross-cultural relationships within and outside the organization. And the most effective ERG programs encourage cross-collaboration between and among affinity groups to take advantage of synergies, encourage the transfer of knowledge, and fuel business objectives .
At GameStop
The executive sponsors of several GameStop ERGs are allies (as opposed to personally representing the cultural affiliation or commonality around which the ERG was formed). So allyship is part of the fabric of those groups.
Also, many GameStop associates are members of multiple ERGs, signaling both intersectionality and a broad commitment on the part of these employees to diversity and inclusion.
GameStop fosters collaboration among ERGs by engaging them in key business events. For example, ERG leaders participate in GameStop’s annual conferences for store leaders and field leaders to promote membership, network, and raise awareness. GameStop ERGs also jointly host an inclusive leadership summit for the professional development of associates from across the business.
7. Align ERGs on Business Initiatives
To encourage buy-in at all levels of the organization, it’s critical for ERGs to align their goals on company objectives such as
- Recruiting – Attending career fairs, sharing job openings with their networks, and referring top talent
- Enhancing leadership development – Serving as a proving ground for emerging leaders from among an ERG’s membership, hosting leadership workshops for employees across the organization, and fostering mentorships
- Creating a culture of inclusivity – Embedding inclusivity into the company culture by raising awareness internally and elevating the company’s brand within the communities the ERGs represent.
At GameStop
All ERGs serve as brand ambassadors for GameStop, representing the company at recruiting events and on social media. By having diverse representation at their career fair booths, GameStop attracts more diverse candidates to learn about the company. And they’ve seen an increase in internal referrals, which in turn decreases staffing and recruiting fees.
GameStop ERGs have tangibly advanced leadership growth in several ways, including
- A structured program for emerging women leaders, which has helped 20 of its graduates earn promotions across the organization
- An informal mentoring program that overlaps with multiple ERGs to give younger staff members an opportunity for growth.
GameStop encourages ERGs to lead and participate in community activities, giving members a new forum to engage with co-workers while positively impacting their communities.
They engage in community service and sponsor a range of charitable and community programs, many of which intersect with the company’s industry such as Toys for Tots and therapeutic gaming. Through these activities, GameStop ERGs effectively build the brand and reach new potential customers.
Where Employee Experience Meets Business Outcomes
Employee resource groups have evolved from employee support networks created to achieve diversity and inclusion to a strategic resource that enhances business outcomes.
By following these best practices, your organization can empower ERGs to become a vital component of the employee experience—making you an employer of choice and connecting you to top talent and new markets.
Need help tracking ERG metrics? See how Affirmity’s ERG management software gives you visibility into membership and budgets, or contact us for more information.
Meet the Experts


Juna Jones-Moore is formerly the Director of Diversity & Inclusion at GameStop, a global retailer of multichannel video games, consumer electronics, and more with more than 5,800 stores in 14 countries. GameStop’s commitment to diversity and inclusivity is a critical component of its corporate culture, as evidenced by its active support for a network of 8 employee resource groups.
D&I expert Pamela Pujo led diversity strategies and guided a network of ERGs at American Airlines. She has managed and led diversity awareness education programs across functional and departmental lines, including talent management, professional development, and business development. As a Diversity Advocate with Affirmity, she helps clients optimize their diversity and inclusion programs through strategic consulting and workforce data insights.
